Insights > Article > Posted: 2023-Nov-16, Updated: 2025-Oct-28
The Hidden Benefits of Window Glass: Enhancing Your Home's Efficiency

In this article:
Why glass matters
Upgrade Your Windows: Say goodbye to ordinary windows and hello to high-quality glass options that can transform your home. Investing in top-quality glass can improve comfort, security, and functionality.
Customisation is Key: Some manufacturers offer a wide range of options, while others may have a limited selection. Research and compare to find the perfect glass for your home.
The technology behind modern windows
Advancements in window technology have revolutionised home design, offering solutions that can be customised for each room.

Key Innovations:
- Thickness and Strength: Glass can be ordered in various thicknesses and strengths for enhanced durability.
- Special Coatings: Coatings can reflect, absorb, and provide shade and privacy.
- Gas Fills: Gases like argon, krypton, and xenon improve insulation by reducing heat transfer.
- Electrostatic Control: Some glass can change colour and shade with an electrostatic charge.
Glazing: enhancing insulation
Window glazing refers to the glass framed within a window (IGUs - insulated glass units). Multiple panes with air or gas spaces in between significantly improve insulation.
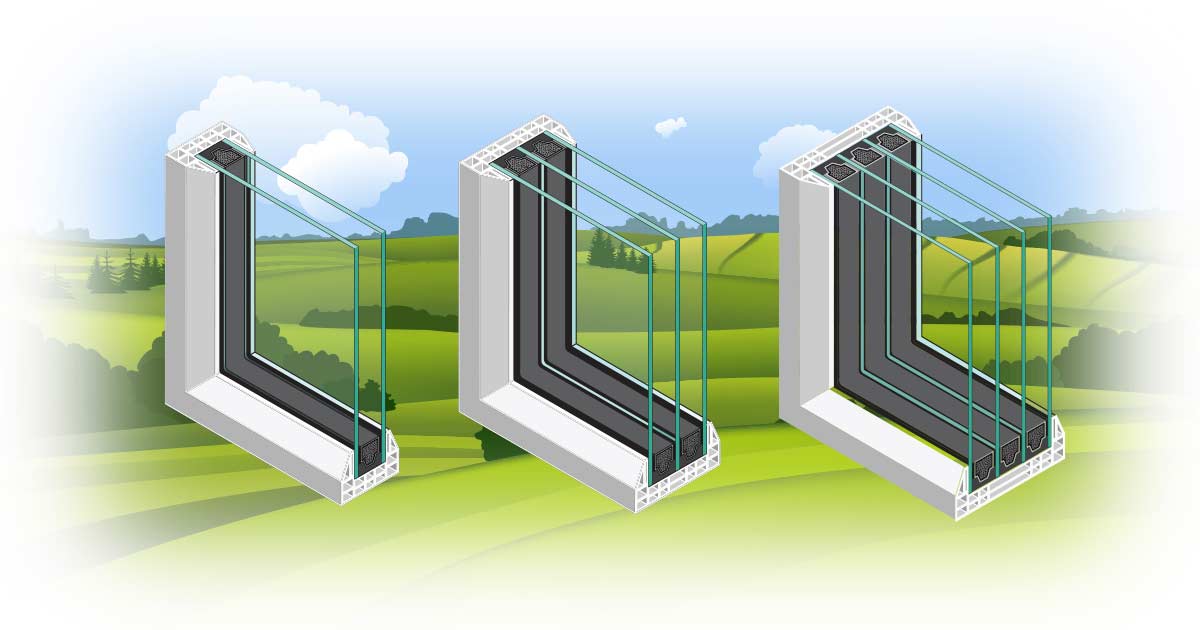
Types of Glazing:
- Double-Glazed Glass: Standard in Canada, offering good insulation.
- Triple and Quadruple Glazing: Available for higher energy efficiency, each additional pane increases insulation but reduces light transmission.
Window spacers (spacer bars)
Spacers separate panes of glass in a window insulated glass unit (IGU). They play a crucial role in the window's insulating properties by maintaining the correct distance between panes and reducing heat transfer.

Common Spacer Technologies:
- Super Spacer®: Uses a high-performance acrylic adhesive and foam spacer along with a moisture vapour seal for durability and thermal performance.
- Intercept® Spacer: Features a one-piece, tin-plated or stainless steel, U-channel design that absorbs flexing when temperatures shift.
- Swiggle® Spacer System: Consists of an aluminium or stainless steel "swiggle" between a butyl rubber seal.
- Aluminium Spacer: Rigid but prone to seal failure, often found in older windows.
Glass fills
The space between panes in insulated glass units can be filled with gases to improve insulation.
Types of Gas Fills:
- Argon: Most commonly used, cost-effective, and optimal at about ½ inch spacing.
- Krypton: More efficient than argon, used in thinner spaces but more expensive.
- Xenon: Offers the best insulation but is the most expensive, typically used in homes with extensive window areas.
Glass coatings
Low-Emissive (Low-E) Glass has a microscopically thin layer of silver that reduces heat flow. Different types of Low-E glass offer varying balances of solar gain, light transmission, and UV blocking.

Common Types:
LoE 180: Ideal for maximising solar gain and light transmission, reducing winter energy costs.
- U-factor: 0.31
- SHGC: 0.68
- Light Transmission: 79%
- UV Blocking: 70%
LoE 272: Balances summer cooling and winter heating, blocking 84% of UV rays.
- U-factor: 0.30
- SHGC: 0.41
- Light Transmission: 72%
- UV Blocking: 84%
LoE 366: Best for climates with extreme temperatures, offering high solar control and visibility.
- U-factor: 0.29
- SHGC: 0.27
- Light Transmission: 65%
- UV Blocking: 95%
Privacy enhancement
Privacy can be managed with various glass treatments:
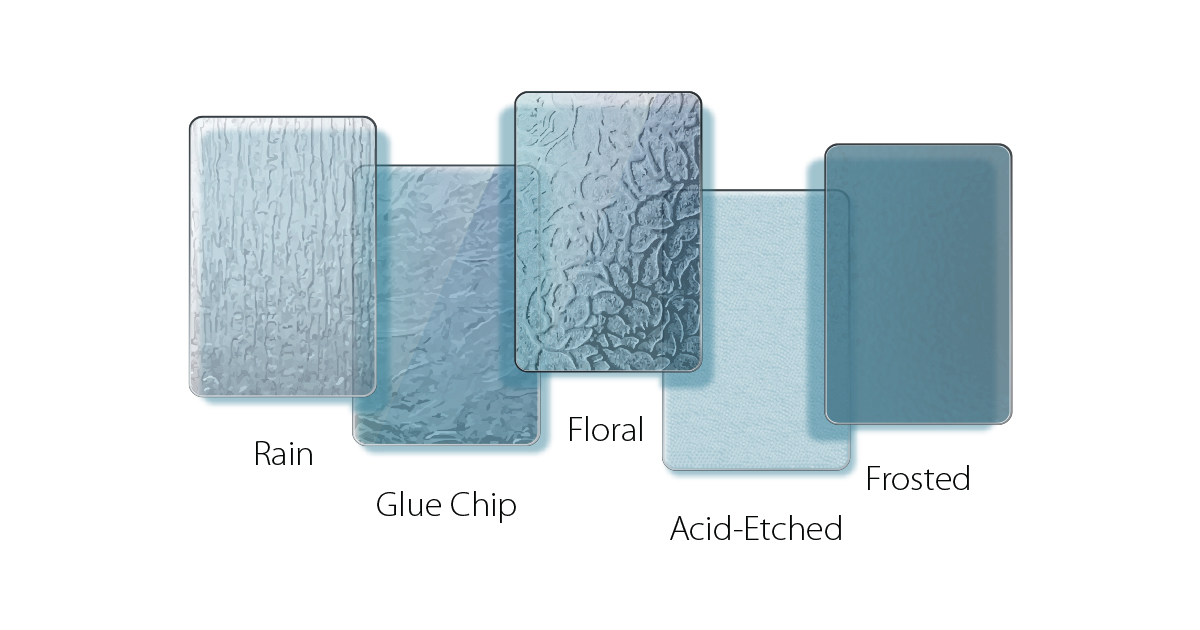
- Textured Glass: Provides light diffusion and decorative effects.
- Frosted Glass: Reduces visibility and is often used in bathrooms.
- Integrated Blinds: Built-in blinds offer privacy and insulation.
- Smart Windows: React to natural light levels to control heat gain, lighting, and privacy.
Durability & security
For added security, different types of processed glass can help protect your property:
- Laminated Glass: Made by bonding layers of glass with resin, holding in place rather than shattering when hit.
- Tempered Glass: About five times stronger than regular glass, making it difficult and loud to break.
Noise reduction
While creating soundproof glass windows isn't possible, several methods can reduce noise:
- Glass Thickness: Thicker glass can help block noise.
- Pane Spacing: Larger spacing between panes reduces sound transmission.
- Laminated Glass: Adds an extra layer of noise reduction.
- Offset glazing: Uses two different glass thicknesses to cancel out highway noise.
Tints
Tinted glass can help manage solar heat gain, reduce glare, and provide additional privacy.
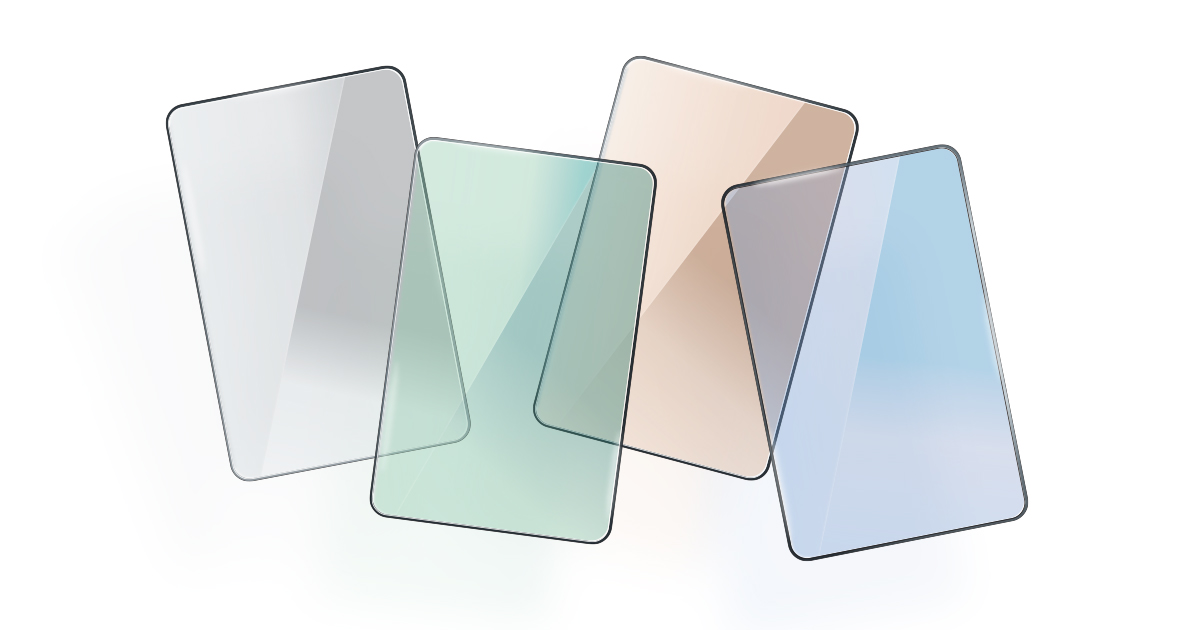

Types of Tints:
- Colour Tints: Available in grey, green, bronze, and blue. These colours are produced by adding metal oxides to float glass during manufacture.
- Visual Transmittance (VT): Tints affect the amount of light passing through the glass. High VT allows more light in, potentially reducing lighting costs, while low VT can increase privacy and reduce glare.
Maintenance
Modern windows are designed to be durable and low-maintenance:
- Hard Glass: Less prone to scratching due to the addition of substances like lead.
- Self-Cleaning Glass: Coatings that prevent dirt from sticking, making cleaning easier.
- Insulation: High-quality insulation reduces condensation and staining.
The strategic glazer: Tailoring windows to your home’s layout
Not every window in your home should be the same. To maximise comfort and minimise energy bills, you should choose your glass packages based on the "micro-climates" of each room.
1. The "Compass" Strategy (Orientation)
The sun affects your home differently depending on which way a room faces. A one-size-fits-all approach often leads to rooms that are either freezing in the winter or like a greenhouse in the summer.
South-Facing Rooms (The Heat Trap): These get the most direct sunlight.
- The Strategy: Use LoE-366 glass. It has three layers of silver coating that block up to 95% of the sun’s heat while letting light through. This prevents your AC from working overtime in July.North-Facing Rooms (The Heat Leaks): These get almost no direct sun and are often the coldest rooms in the house.
North-Facing Rooms (The Heat Leaks): These get almost no direct sun and are often the coldest rooms in the house.
- The Strategy: Use LoE-180 (High Solar Gain) glass. It is designed to act like a thermal blanket, trapping as much heat as possible inside the room. Since there is no "sun heat" to block, you want the highest insulation factor (U-value) possible.
East/West Bedrooms: These face the low, blinding sun in the morning or evening.
- The Strategy: Consider tinted or Neat® naturally clean glass to reduce glare and ensure the sun doesn't wake you up at 5:00 AM or overheat your bedroom right before you go to sleep.
2. The Condensation Strategy (Combating "Sweating")
Condensation on the inside of a window isn't a window leak—it’s a sign that the glass surface is too cold. When warm, humid indoor air hits cold glass, it turns into water.
- The "Warm Edge" Defense: Ensure your windows use a non-metal spacer bar (like a foam or structural plastic). Metal spacers conduct cold from the outside, chilling the edges of the glass and causing a ring of condensation.
- The Gas Buffer: Triple-pane windows with Krypton gas are the ultimate defense against condensation. Because Krypton is denser than Argon, it keeps the inner pane of glass significantly closer to your home’s room temperature.
- The Airflow Rule: Strategy isn't just about glass; it's about placement. Ensure your floor vents aren't covered by heavy drapes, as stagnant air against the glass is the primary cause of "sweat" buildup.
3. The Noise & Security Strategy
If your home faces a busy street or a park, your strategy should focus on Laminated Glass rather than just standard tempered glass.
- Sound Dampening: Ask for dissimilar glass thickness. By using one pane of 3mm glass and one pane of 5mm glass in the same unit, you break different sound frequencies, making your home significantly quieter than using two panes of the same thickness.
- Forced Entry: Laminated glass is nearly impossible to break through quickly. It’s the same technology used in car windshields—the glass may crack, but it stays bonded to an inner plastic layer, keeping intruders out.
Summary
Choosing the right glass for your home can significantly impact comfort, energy efficiency, and security. Consult with a window specialist to explore the best options for your needs, and transform your living space with the perfect glass solution.
Related articles
Need more information?
Looking for new windows? Bayview Windows offers a wide range of high-quality glass options to keep your home cool in summer, warm in winter, and quiet year-round. From energy-efficient low-E glass to strong tempered glass, we have the perfect solution for you.
Ready to upgrade? Call us today! Our experts will help you choose the ideal glass for your needs. Enhance your home's comfort, efficiency, and security with Bayview Windows. Don't wait—transform your home now!