Insights > Energy Efficiency
Energy Star Labels
INFOGRAPHIC
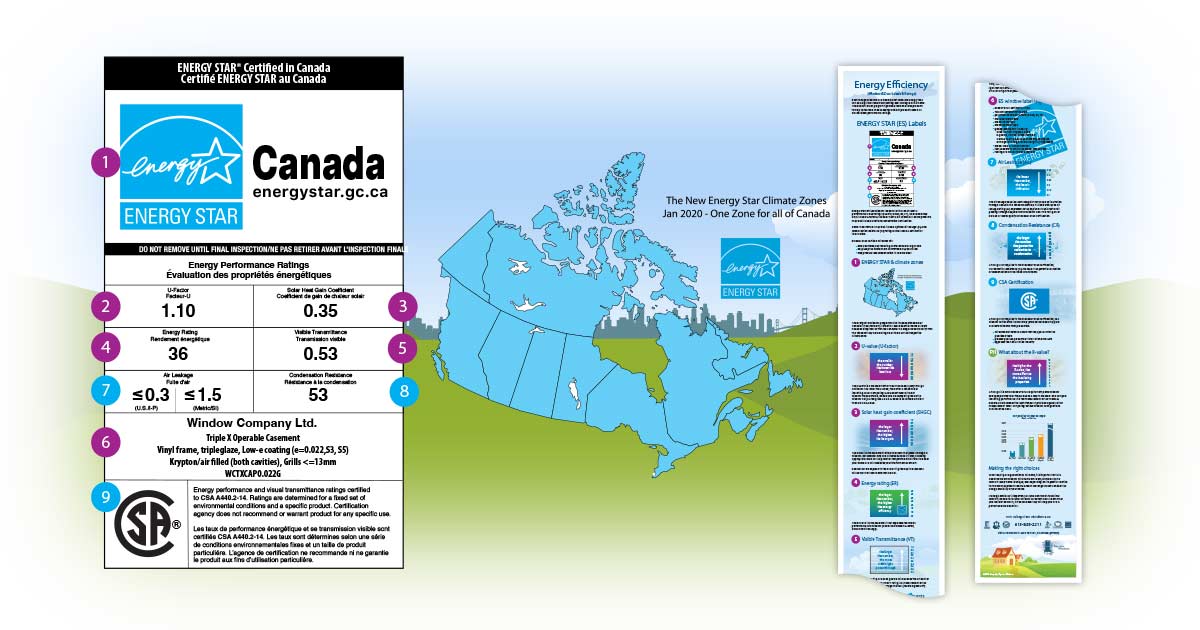
In Canada, energy-efficient windows begin with ENERGY STAR certification. These certified windows meet or exceed high-efficiency standards, ranking in the top 15 to 30 percent for energy performance in their class. Every ENERGY STAR-certified product comes with a temporary label, packed with ratings that help both suppliers and consumers understand what they’re purchasing or installing.
Energy Star Labels
Understanding Ratings
Navigating window and glass ratings can be perplexing, as higher numbers are preferred in some cases while lower numbers are preferred in others. To assist you, here are some helpful tips.
Energy Star
CDN Climate Zone
Even though windows do not consume energy, they can be a significant source of heat loss in a home. ENERGY STAR qualified windows will save you money by reducing the overall annual energy costs. ENERGY STAR windows will also help keep your home more comfortable all-year-round and may have less condensation in cold weather compared with a conventional non-certified product.
Energy Star
Comparing Products

When deciding where to buy your windows, finding comparative information is straightforward. However, interpreting this data can be overwhelming.
Performance Rating
Visual Transmittance (VT)
The amount of light you let into your home is a matter of personal taste. When replacing your windows, knowing what VT is and how to control it will help you get it right.
Performance Rating
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
Let the sun shine in, or not. The Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) measurement can help you achieve a desired increase or decrease in the amount of solar radiation (heat) passing through a window into your home.
Performance Rating
Energy Star (ER)
Although windows and doors don’t consume energy themselves, they can be a significant source of energy loss. If you're purchasing windows with energy efficiency in mind, the ER helps you make standardized product comparisons.
Performance Rating
Air Leakage (AL)
Air leakage (AL) is becoming an increasingly important factor when selecting energy-efficient windows and doors, especially for homeowners in cold climates like Ottawa. With rising energy costs and a focus on energy efficiency, understanding AL can help you choose products that reduce drafts and maintain indoor comfort. But what exactly is air leakage, and why should you care?
Performance Rating
R-value of Insulation
Move over, traditional window specs – the R-value is becoming a popular measurement in the world of window sales! Though it's been around for a while, this rating is gaining traction as an indicator of window efficiency. But why the sudden surge in popularity? Keep reading to find out.
Performance Rating
U-factor (U-Value)
When choosing windows, two key metrics to consider are the U-factor (or U-value) and the Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC). Understanding these can help you make informed decisions for better home comfort and energy efficiency.
Glass Performance
Spectrally Selective Coatings

Spectrally selective coatings are advanced coatings applied to glass that filter and control the amount of solar energy that enters a building.
Glass Performance
Low-E Coatings

Low-emissivity (low-E or LoE) glass, commonly known as LoE glass, is engineered to reflect radiant heat, significantly improving the thermal efficiency of windows. Emissivity measures how much heat a glass surface transfers through it.
Glass Performance
Gas Between the Panes
Modern windows are much more than mere openings in our walls; they play a crucial role in our home's energy efficiency and comfort. Have you ever wondered why some windows seem to keep your home warmer in winter and cooler in summer? The secret lies in the type of gas used between the panes of glass. Choosing the right gas can significantly impact your home's energy consumption and overall comfort. Let's dive into the fascinating world of gas-filled windows and discover how they work and why they matter.
Windows
Entrance Doors
Patio Doors
Energy Efficiency
Extreme Temperatures
Installation
Bayview Windows
Stay Cool This Summer: The Benefits of Energy-Efficient Windows for Your Home
Making Windows Energy
Efficient - INFOGRAPHIC
Efficient - INFOGRAPHIC
Keep Energy Costs Down and Comfort Up with Energy-Efficient Windows
Energy Star Labels
INFOGRAPHIC
INFOGRAPHIC
Energy Star Labels
Understanding Ratings
Understanding Ratings
Energy Star
CDN Climate Zone
CDN Climate Zone
Energy Star
Comparing Products
Comparing Products
Performance Rating
Visual Transmittance (VT)
Visual Transmittance (VT)
Performance Rating
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
Solar Heat Gain (SHGC)
Performance Rating
Energy Star (ER)
Energy Star (ER)
Performance Rating
Air Leakage (AL)
Air Leakage (AL)
Performance Rating
R-value of Insulation
R-value of Insulation
Performance Rating
U-factor (U-Value)
U-factor (U-Value)
Glass Performance
Spectrally Selective Coatings
Spectrally Selective Coatings
Glass Performance
Low-E Coatings
Low-E Coatings
Glass Performance
Gas Between the Panes
Gas Between the Panes
